RapidSMS Architecture Overview¶
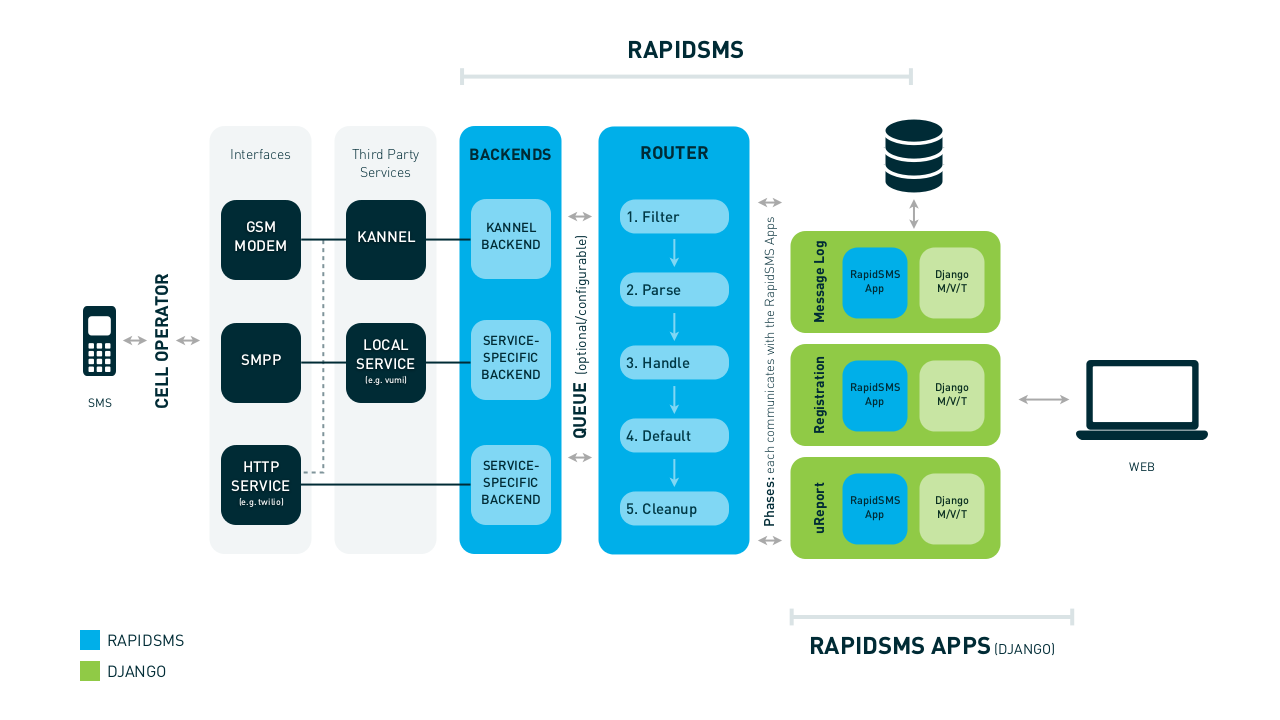
You can also view the full-sized version.
Introduction¶
RapidSMS is divided into a few core components:
If you are new to RapidSMS most likely you will want to develop Applications.
Applications¶
RapidSMS applications, or “apps”, perform one or more of the following functions:
- Performs your business logic
- Handles and responds to messages
- Extends the data model
- Creates a web interface with Django views and templates
For example, a registration application may provide a messaging protocol for users to register themselves into the system. In general, you’ll probably be writing applications more than anything else. Please see the application documentation for more information.
RapidSMS represents the entities it communicates with using Contacts, which you’ll also want to understand before writing applications.
Backends¶
Backends receive messages from external sources and deliver messages from applications to external sources. Example backends include:
- Using Kannel to communicate to a GSM modem connected over USB or Serial
- Using Twilio or Clickatell to send and receive SMS messages over HTTP
Please see the backend documentation for more information.
Router¶
The router is the message processing component of RapidSMS. It provides the infrastructure to receive incoming, send outgoing messages, and gluing together your applications and backends. RapidSMS provides several built-in routers to use based on the needs of your application.
Please see the router documentation for more information.
